


| CARBOHYDRATES | PROTEINS | LIPIDS | NUCLEIC ACIDS | |
| Elements present | C, H, O | C, H, O, N | C, H, O | C, H, O, N, P |
| Sub Units | sugar (monosaccharides) | amino acids | glycerol & fatty acids, steroids | nucleotides |
| Examples | Glucose, Sucrose, Glycogen, Starch, Cellulose, Chitin | Enzymes, Keratin, Haemoglobin, Insulin, Antibodies | fats, oils, cholesterol, oestrogen, testosterone | DNA, mRNA, tRNA, rRNA |
| Monosaccharide (glucose) | 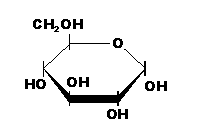
|
|---|---|
| Amino acid (general) | 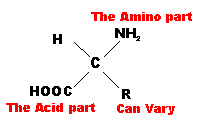
|
| Triglyceride | 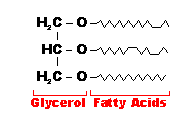
|
| Nucleotide | 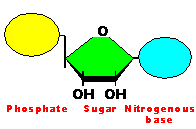
|
 Once the substrate has entered the active site (the key is in the lock), an enzyme-substrate complex has formed. Within this, minor rearrangements of the enzyme's weak bonds can occur, twisting the substrate into a position where the chemical reaction can procede much more rapidly than it otherwise would have done.
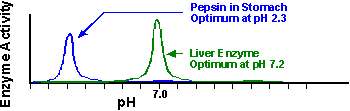
Once the substrate has entered the active site (the key is in the lock), an enzyme-substrate complex has formed. Within this, minor rearrangements of the enzyme's weak bonds can occur, twisting the substrate into a position where the chemical reaction can procede much more rapidly than it otherwise would have done.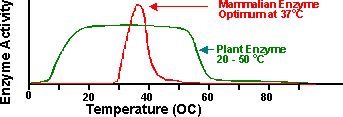

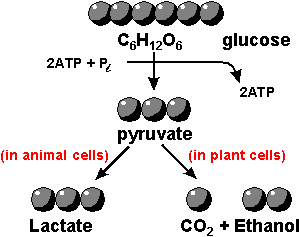
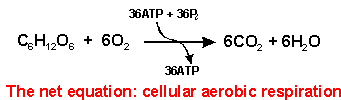
| DIFFUSION | OSMOSIS | ACTIVE TRANSPORT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy requirements | ATP not required | ATP not required | ATP required |
| Distance of travel | Solutes and gases- long distances | Solvent (water)- short distances | Short distances |
| Speed of process | Rapid in gases, slow in solution | Slow process | Rapid process |
| Definition | Transport of gases or dissolved substances (solutes) in solution from a region of high concentration to a region of lower concentration of the transported substance. | Transport of a solvent (water) through a semipermeable membrane from a solution of low solute concentration to a solution of higher solute concentration. | Transport of a substance from lower to higher concentration of that substance, using energy from the cell, through a living cell membrane. |
| Examples | Uptake of oxygen by a cell performing aerobic respiration. Oxygen continues to diffuse into the cell as O2 is removed by respiration. | The movement of water into cells of a marine (salt water adapted) animal placed in fresh water. May eventually cause cells to swell and burst. | Transport of glucose against its concentration gradient from the gut lumen into the cells lining the intestine. |